Menstruation-
Menstruation is a natural biological process in which the lining of the uterus is shed through vaginal bleeding.
It typically occurs in females of reproductive age, starting around puberty and continuing until menopause.
Menstrual cycles generally last about 28 days, though variations are common. The cycle involves hormonal changes, with the release of an egg from the ovaries, and the preparation of the uterus for a potential pregnancy. If pregnancy doesn’t occur, the uterine lining is expelled during menstruation.
Menstrual blood consists of blood, tissue, and fluids. It’s a crucial aspect of the reproductive system, indicating a woman’s fertility and overall health.
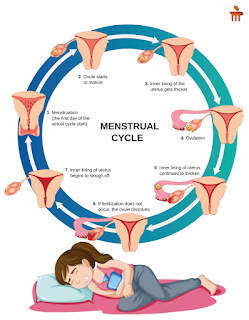
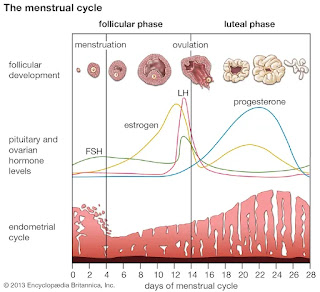
The menstrual cycle is a crucial aspect of female reproductive health. It involves a series of hormonal changes and events in the ovaries and uterus, typically lasting about 28 days, although it can vary. The key phases are:
1. Menstrual Phase (Days 1-5): The shedding of the uterine lining, marked by menstrual bleeding.
2. Follicular Phase (Days 6-14): Follicles in the ovaries mature, and one releases an egg during ovulation.
3. Ovulatory Phase (Day 14): The release of the egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube, making it available for fertilization.
4. Luteal Phase (Days 15-28): The empty follicle transforms into a structure called the corpus luteum, producing progesterone to prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy. If fertilization doesn’t occur, the cycle restarts.
Menstruation Importance:
Hormonal Regulation:
Hormones like estrogen and progesterone, which fluctuate during the cycle, play vital roles in maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being.
Uterine Health:
Menstruation helps maintain a healthy uterine lining, and the cycle allows for regular shedding and renewal.
Ovulation Tracking : Monitoring the menstrual cycle is often used in family planning, whether to achieve or avoid pregnancy.
Overall Health: Irregularities in the menstrual cycle can sometimes signal underlying health issues, making it a valuable indicator of a woman’s general well-being.
Understanding one’s menstrual cycle can aid in reproductive planning, monitoring hormonal health, and addressing potential concerns.
Menstruation can be associated with various challenges and discomforts. Here are some common menstruation-related issues:
1. Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS):
Many women experience physical and emotional symptoms like bloating, mood swings, and breast tenderness in the days leading up to menstruation.
Symptoms: Mood swings, bloating, breast tenderness, fatigue.
Cause: Hormonal changes before menstruation.
Treatment: Lifestyle changes, stress management, medications for severe cases.
2. Menstrual Cramps:
Painful uterine contractions can cause abdominal cramps during menstruation, known as dysmenorrhea.
Symptoms: Pain in the lower abdomen, backache, nausea.
– Cause: Uterine contractions during menstruation.
– Treatment: Over-the-counter pain relievers, heat therapy, exercise.
3. Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Menorrhagia):
Some women may experience excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding, which can lead to fatigue and anemia.
Symptoms: Excessive bleeding, longer periods, fatigue.
Cause: Hormonal imbalances, uterine fibroids, blood disorders.
Treatment: Hormonal medications, surgical interventions.
4. Irregular Menstrual Cycles:
Cycle length variations are common, but irregularities can be caused by factors like stress, hormonal imbalances, or underlying health conditions.
Symptoms: Inconsistent or unpredictable periods.
Cause: Stress, weight changes, hormonal imbalances.
Treatment: Hormonal contraceptives, lifestyle adjustments.
5. Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD):
A severe form of PMS characterized by intense mood swings, anxiety, and irritability.
Symptoms: Mood swings, bloating, breast tenderness, fatigue.
– Cause: Hormonal changes before menstruation.
– Treatment: Lifestyle changes, stress management, medications for severe cases.
6. Menstruation Endometriosis:
A condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, causing pain, inflammation, and potential fertility issues.
7. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
A hormonal disorder that can lead to irregular periods, ovarian cysts, and other symptoms.
8. Menstruation Amenorrhea:
The absence of menstruation, which may be due to factors like pregnancy, extreme weight loss, or hormonal imbalances.
Symptoms: No menstrual periods.
Cause: Pregnancy, hormonal imbalances, excessive exercise.
Treatment: Address underlying causes, hormone therapy.
9. Menstrual Migraines:
Some women may experience migraines triggered by hormonal changes during menstruation.
10. Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB):
Abnormal uterine bleeding not associated with structural abnormalities, often due to hormonal imbalances.
It’s important to note that while these issues are common, they can vary in severity and impact from person to person. If someone is experiencing significant discomfort or unusual symptoms, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and management.
11. Premature Ovarian Failure (POF):
Symptoms: Irregular periods, hot flashes, mood changes.
Cause: Early depletion of ovarian follicles.
Treatment: Hormone replacement therapy, fertility treatments.
It’s crucial to seek professional medical advice for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment based on individual circumstances.
Maintaining a healthy menstruation cycle involves adopting lifestyle habits that support overall well-being. Here are some ways to promote a healthy menstrual cycle:
1. Balanced Diet:
– Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
– Adequate intake of iron-rich foods to prevent anemia.
2. Regular Exercise:
– Engage in moderate physical activity to help regulate hormones and reduce stress.
– Yoga and aerobic exercises can be beneficial.
3. Adequate Hydration:
– Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and support bodily functions.
4. Proper Stress Management:
– Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or mindfulness.
5.Menstruation Adequate Sleep:
– Ensure you get enough sleep each night to support overall health.
6. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
– Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
7. Limit Caffeine and Alcohol:
– Moderate consumption of caffeine and alcohol as excessive intake may affect hormonal balance.
8. Menstruation Regular Health Check-ups:
– Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider for preventive care and to address any concerns.
9. Menstruation Personal Hygiene:
– Maintain good menstrual hygiene practices to prevent infections.
10. Menstruation Hormonal Balance:
– If necessary, consult with a healthcare professional to address hormonal imbalances.
Remember, individual needs vary, and it’s essential to tailor these suggestions based on your specific health conditions. If you have concerns about your menstrual health, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance tailor these suggestions based on your specific health conditions.
For related to women’s health exercises click the link-https://www.womaniyas.com/2024/02/exercising-during-menstruation.html