Shortened menstrual cycle or frequent periods-
A shortened menstrual cycle refers to a menstrual cycle that occurs more frequently than the typical 28-day cycle. Normally, menstrual cycles range from 21 to 35 days, with menstruation lasting about 2 to 7 days.
If your menstrual cycle consistently occurs more frequently than every 21 days, it’s considered a shortened cycle. Here are some details about shortened menstrual cycles:
1. Duration: A shortened menstrual cycle means that the time between the start of one period and the start of the next is shorter than usual.
For example, instead of the typical 28-day cycle, you may experience a cycle that lasts only 21 or 24 days.
2. Frequency of Periods:
With a shortened menstrual cycle, you may find yourself getting your period every two weeks or even more frequently.
3. Blood Flow:
Despite the shortened duration between periods, the flow of blood during menstruation may be similar to what you experience during a regular cycle.
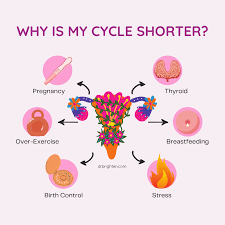
4. Possible Causes:
Several factors can contribute to a shortened menstrual cycle, including hormonal imbalances, stress, thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), perimenopause, uterine abnormalities, certain medications, excessive exercise, rapid weight loss, and dietary factors.
5. Symptoms:
Along with the shortened cycle, you may experience other symptoms such as irregular bleeding, spotting between periods, changes in menstrual flow, pelvic pain, mood swings, fatigue, and changes in appetite.
Experiencing a shortened menstrual cycle can be accompanied by various symptoms, which may vary depending on the underlying cause.
Here are details about symptoms commonly associated with shortened menstrual cycles:
1. Increased Frequency of Periods:
The primary symptom of a shortened menstrual cycle is having periods more frequently than the typical 21 to 35 days.
This means you may find yourself getting your period every two weeks or even more often.
2. Irregular Bleeding:
Along with more frequent periods, you may also experience irregular bleeding patterns.
This could include spotting between periods or changes in the duration or intensity of menstrual flow.
3. Pelvic Pain or Discomfort:
Some individuals with shortened menstrual cycles may experience pelvic pain or discomfort, which can range from mild to severe.
This pain may occur during menstruation or throughout the menstrual cycle.
4. Changes in Menstrual Flow:
You may notice changes in the amount or consistency of menstrual blood during your shortened menstrual cycles. This could include heavier or lighter flow than usual, as well as changes in the color or texture of menstrual blood.
5. Mood Swings and Emotional Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations associated with shortened menstrual cycles can sometimes lead to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, or depression.
These emotional changes may occur in conjunction with menstruation or throughout the menstrual cycle.
6. Fatigue and Low Energy:
Some individuals may experience fatigue or low energy levels as a result of hormonal imbalances or excessive bleeding associated with shortened menstrual cycles.
7. Changes in Libido:
Hormonal fluctuations can also affect libido or sexual desire.
You may notice changes in your interest or desire for sexual activity during shortened menstrual cycles.
8. Other Symptoms:
Depending on the underlying cause of the shortened menstrual cycles, you may experience additional symptoms such as hair loss, acne, weight changes, headaches, insomnia, or hot flashes.
It’s important to note that while these symptoms are commonly associated with shortened menstrual cycles.
They can also occur due to other factors or medical conditions.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms or menstrual irregularities.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.
They can help identify the underlying cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your needs.
6. Diagnosis:

To determine the cause of a shortened menstrual cycle, your healthcare provider may perform a physical examination, review your medical history, and conduct tests such as blood tests to check hormone levels, ultrasound to evaluate the reproductive organs, and possibly a biopsy if uterine abnormalities are suspected.
7. Treatment:
Treatment for a shortened menstrual cycle depends on the underlying cause.
Hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and address hormonal imbalances.
Other treatments may include medication to manage underlying conditions like PCOS or thyroid disorders, lifestyle changes to reduce stress and promote overall health, and surgical intervention if structural abnormalities are present.
Treatment for a shortened menstrual cycle depends on the underlying cause.
Here’s a detailed overview of treatment options:
1. Hormonal Contraceptives:
Birth control pills are often prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles by stabilizing hormone levels.
These pills can help lengthen the menstrual cycle and reduce the frequency of periods.
They work by suppressing ovulation and providing a steady dose of hormones (estrogen and progestin) to regulate the menstrual cycle.
Other forms of hormonal contraceptives, such as the contraceptive patch, vaginal ring, or contraceptive injection, may also be considered.
2. Hormone Therapy:
In cases where hormonal imbalances are the cause of shortened menstrual cycles, hormone therapy may be recommended.
This involves taking hormone supplements to restore hormonal balance and regulate menstrual cycles.
Hormone therapy may include estrogen therapy, progestin therapy, or a combination of both, depending on individual needs.
3. Treatment for Underlying Conditions:
If a specific underlying condition is identified as the cause of shortened menstrual cycles (such as polycystic ovary syndrome or thyroid disorders), treatment will be targeted towards managing that condition.
This may include medications to regulate insulin levels in the case of PCOS, or thyroid hormone replacement therapy for thyroid disorders.
4. Lifestyle Modifications:
Making lifestyle changes can sometimes help regulate menstrual cycles.
This may include reducing stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation, maintaining a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and ensuring adequate sleep.
5. Surgical Intervention:
In rare cases where structural abnormalities in the reproductive organs are causing shortened menstrual cycles (such as uterine fibroids or polyps), surgical intervention may be necessary to remove or treat these abnormalities.
6. Nutritional Supplements:
Some women may benefit from taking nutritional supplements such as iron, vitamin B12, or folate to address deficiencies caused by excessive menstrual bleeding associated with shortened cycles.
7. Alternative Therapies:
Certain alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or herbal supplements, may be considered as adjunctive treatments to help regulate menstrual cycles.
However, it’s essential to discuss these options with a healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your specific situation.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment if you’re experiencing shortened menstrual cycles or any other menstrual irregularities.
They can help identify the underlying cause of your symptoms and recommend the most appropriate treatment options for your individual needs.
If you’re experiencing a shortened menstrual cycle or any other menstrual irregularities.
it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.
They can help identify the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Getting menstrual cycle in every week –

Experiencing a menstrual cycle every other week, also known as having a shortened menstrual cycle or frequent periods.
It can be concerning and may indicate an underlying health issue.
Here are some potential reasons for this irregularity:
1. Hormonal Imbalance:
Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone, can cause irregular menstrual cycles. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders can contribute to hormonal imbalances.
2. Stress:
High levels of stress can disrupt the hormonal balance in your body, leading to irregular menstrual cycles.
3. Birth Control:
Certain forms of birth control, such as hormonal contraceptives or intrauterine devices (IUDs), can sometimes cause irregular bleeding or spotting.
4. Perimenopause:
As women approach menopause, their menstrual cycles can become irregular, sometimes resulting in more frequent periods.
5. Uterine or Cervical Disorders:
Conditions like fibroids, polyps, or infections in the uterus or cervix can cause abnormal bleeding.
6. Medications:
Some medications, such as anticoagulants or hormone therapy, may affect menstrual cycles.
7. Excessive Exercise or Weight Loss:
Intense physical activity or rapid weight loss can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to irregular periods.
8. Dietary Factors:
Poor nutrition or extreme dieting can impact hormone levels and menstrual regularity.
If you’re experiencing frequent periods or any other menstrual irregularities, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider.
They can evaluate your symptoms, perform any necessary tests, and provide appropriate treatment options based on the underlying cause.
Keeping track of your menstrual cycle patterns and any associated symptoms can also help your healthcare provider make an accurate diagnosis.
For more info visit here also – https://womaniyas.com/2024/03/01/what-are-fibroids-or-uterine-fibroids-or-leiomyomas/
