Ovarian cancer(SILENT KILLER)-
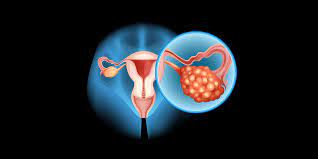
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system. The ovaries are responsible for producing eggs (ova) and hormones, including estrogen and progesterone. Ovarian cancer is a relatively rare but serious and often fatal cancer, as it is often detected at an advanced stage.
Here is some detailed information about ovarian cancer:
Types of Ovarian Cancer:
1. Epithelial Ovarian Cancer (EOC): This is the most common type, accounting for about 90% of all ovarian cancers. It starts in the cells that cover the surface of the ovary.
2. Stromal Cell Tumors: These tumors originate in the ovarian tissue that produces hormones. They are less common than epithelial tumors.
3. Germ Cell Tumors: These tumors develop in the egg-producing cells of the ovary and are more common in younger women.
Risk Factors:(Causes)-
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is not fully understood, and it often develops without a clear explanation. However, several risk factors have been identified that may increase the likelihood of developing ovarian cancer. It’s important to note that having one or more risk factors does not guarantee the development of ovarian cancer, and many women with ovarian cancer have no known risk factors. Here are some factors associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer:
1. Age: Ovarian cancer is more common in older women. The risk increases with age, and it is most frequently diagnosed in women over the age of 63.
2. Family History: A family history of ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer can elevate the risk. Women with first-degree relatives (mother, sister, or daughter) who have had ovarian cancer may be at a higher risk.
3. Inherited Gene Mutations: Mutations in specific genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, are associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer. Women with these genetic mutations have a higher likelihood of developing ovarian cancer.
4. Personal History of Cancer: Women who have had breast, uterine, or colorectal cancer may face a slightly higher risk of ovarian cancer.
5. Inherited Lynch Syndrome: Lynch syndrome, also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), is an inherited condition associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer.
6. Endometriosis: Women with endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, may have a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer.
7. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Prolonged use of estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy (HRT) after menopause may be associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer.
8. Never Having Been Pregnant: Women who have never been pregnant may have a slightly higher risk of ovarian cancer.
9. Talcum Powder Use: Some studies have suggested a potential link between the use of talcum powder in the genital area and an increased risk of ovarian cancer. However, the evidence is not conclusive, and more research is needed to establish a definitive connection.
It’s essential to understand that while these factors may increase the risk, many women diagnosed with ovarian cancer have no known risk factors. Additionally, researchers continue to investigate the complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors that contribute to the development of ovarian cancer.
Regular gynecological check-ups, awareness of symptoms, and discussions with healthcare providers about individual risk factors are crucial for early detection and effective management of ovarian cancer. If you have concerns about your risk or family history, consider seeking genetic counseling to better understand your individual situation.
Symptoms:
– Ovarian cancer is often called the ‘silent killer ‘ because early-stage symptoms may be subtle.
– Common symptoms include abdominal bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty eating or feeling full quickly, and frequent urination.
Ovarian cancer is often referred to as the “silent killer” because symptoms may not be apparent in the early stages, and when they do appear, they can be subtle and easily overlooked. However, it’s important to be aware of potential signs and symptoms. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. Common symptoms of ovarian cancer include:
1. Abdominal or Pelvic Pain: Persistent discomfort or pain in the abdomen or pelvis that is not related to menstruation or normal digestive issues.
2 Bloating: Unexplained and persistent bloating, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms.
3. Difficulty Eating or Feeling Full Quickly: Changes in appetite, difficulty eating, or a feeling of fullness even after consuming small amounts of food.
4. Frequent or Urgent Urination: Increased frequency of urination, especially if it is accompanied by a sense of urgency.
5. Changes in Bowel Habits: Any significant changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea, that persist for an extended period.
6. Unexplained Weight Loss: A noticeable and unexplained weight loss, especially if it occurs rapidly.
7. Fatigue: Persistent fatigue or low energy levels that are not alleviated by rest.
8. Back Pain: Pain in the lower back can be a symptom, although it is less specific and can be caused by various conditions.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can be caused by various conditions, and experiencing them does not necessarily mean you have ovarian cancer. However, if these symptoms are persistent, frequent, and unrelated to other known health issues, it is essential to seek medical attention for a thorough evaluation.
Furthermore, ovarian cancer is more common in older women, and women with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer may have an increased risk. If you are at a higher risk due to family history or other factors, it is advisable to discuss appropriate screening measures with your healthcare provider.
Early detection of ovarian cancer can significantly improve treatment outcomes. If you suspect any symptoms or have concerns about your health, consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. Regular gynecological check-ups are crucial for women’s health, especially for those at higher risk.
Diagnosis:
– No routine screening test is available for ovarian cancer, making early detection challenging.
– Diagnosis often involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scans), and blood tests (CA-125 tumor marker).
Treatment:
– Surgery is a common treatment for ovarian cancer, involving the removal of the tumor and affected tissues.
– Chemotherapy is often used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
– Radiation therapy may be used in specific cases.
Prognosis:
– Prognosis depends on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed. Early detection generally leads to better outcomes.
– Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage, making it challenging to treat.
Prevention:
– There is no foolproof way to prevent ovarian cancer, but factors such as oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, and breastfeeding may reduce the risk.
– Regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms are crucial for early detection.
Preventing ovarian cancer involves adopting certain lifestyle choices and, in some cases, considering risk-reducing measures, particularly for individuals with a family history or other risk factors. It’s important to note that while these strategies may help reduce the risk, they do not guarantee complete prevention. Here are some general guidelines for ovarian cancer prevention:
1. Oral Contraceptives (Birth Control Pills): Long-term use of oral contraceptives has been associated with a reduced risk of ovarian cancer. Discuss the potential benefits and risks with your healthcare provider.
2. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: The number of pregnancies a woman has and the duration of breastfeeding may influence ovarian cancer risk. Women who have had multiple pregnancies and breastfeeding experiences may have a lower risk.
3. Tubal Ligation and Hysterectomy: Surgical procedures like tubal ligation (having your tubes tied) and hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) have been associated with a decreased risk of ovarian cancer. However, these procedures are typically done for other medical reasons and are not recommended solely for ovarian cancer prevention.
4. Healthy Diet: Adopting a healthy and balanced diet may contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk of ovarian cancer. Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars.
5. Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity has been linked to a lower risk of various cancers, including ovarian cancer. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
6. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight or obese is associated with an increased risk of several types of cancer, including ovarian cancer. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise can be beneficial.
7. Avoiding Talcum Powder in the Genital Area: Some studies have suggested a possible link between the use of talcum powder in the genital area and an increased risk of ovarian cancer. While more research is needed to establish a definitive connection, if concerned, you may choose to avoid using talcum powder in this area.
8. Genetic Counseling and Testing: If you have a family history of ovarian cancer or other related cancers, genetic counseling and testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations may be considered. Identifying these mutations can help assess the risk and guide preventive measures.
It’s important to note that there is no foolproof way to prevent ovarian cancer, and the effectiveness of some preventive strategies may vary from person to person. Regular gynecological check-ups and discussions with healthcare providers are essential, especially for individuals with an increased risk. If you have concerns about ovarian cancer prevention or your individual risk, consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance based on your health history and family background.
If you suspect any symptoms or have concerns about ovarian cancer, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. Regular gynecological check-ups are important for women, especially those with risk factors or a family history of ovarian cancer.
World Ovarian Cancer Day( 8th May)-
World Ovarian Cancer Day is an annual global awareness initiative dedicated to raising awareness about ovarian cancer, educating the public, and advocating for improved resources for prevention, early detection, and treatment. The day is observed on May 8th each year. Here is some detailed information about World Ovarian Cancer Day:
Objective:
The primary objectives of World Ovarian Cancer Day include:
1. Raising Awareness: The day aims to increase public understanding of ovarian cancer, its symptoms, risk factors, and the importance of early detection.
2. Providing Information: World Ovarian Cancer Day serves as an opportunity to disseminate accurate and up-to-date information about ovarian cancer to the public, healthcare professionals, and policymakers.
3. Supporting Patients: The day is a platform to show solidarity with those who are currently battling ovarian cancer, as well as to honor and remember those who have lost their lives to the disease.
4. Advocating for Resources: Advocacy efforts on this day focus on urging governments, healthcare organizations, and communities to allocate resources for research, improved diagnostics, and better treatment options for ovarian cancer.
History:
World Ovarian Cancer Day was first established in 2013. It is a collaborative effort led by ovarian cancer advocacy organizations, healthcare professionals, and individuals affected by ovarian cancer from around the world. The initiative was created to address the lack of awareness about ovarian cancer compared to other cancers and to emphasize the importance of early detection.
Activities and Initiatives:
1. Educational Campaigns: Organizations and individuals participate in various educational initiatives, including distributing information about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors, and preventive measures.
2. Community Outreach: Local events such as seminars, workshops, and health fairs are organized to engage communities and provide them with opportunities to learn more about ovarian cancer.
3. Social Media Campaigns: Advocates often use social media platforms to share information, personal stories, and messages of support. The hashtag #WorldOvarianCancerDay may be used to amplify the campaign’s reach.
4. Fundraising Events: Many organizations use this day to raise funds for ovarian cancer research, support programs, and patient advocacy.
5. Wearing Teal: Teal is the designated color for ovarian cancer awareness. Supporters are encouraged to wear teal clothing or accessories to show solidarity and raise awareness.
Teal Ribbon:
The teal ribbon is the international symbol for ovarian cancer awareness. It is prominently featured during World Ovarian Cancer Day and throughout the month of May, which is recognized as Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month in various countries.
Participation in World Ovarian Cancer Day is open to individuals, healthcare professionals, advocacy groups, and organizations around the world. By uniting efforts on this day, the hope is to make significant strides in raising awareness and improving outcomes for those affected by ovarian cancer.
For more women’s related information click here- https://womaniyas.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=15&action=edit

.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)